HKUST Identifies Novel Host Factors that Facilitates SARS-CoV-2 Entry
A research team led by Prof. GUO Yusong, Associate Professor of the Division of Life Science at the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST), recently made a novel discovery related to the coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) that causes COVID-19. The team identified new host factors that interact with the receptor binding domain of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein to promote viral entry. This finding offers valuable mechanistic insights and potential therapeutic strategies against SARS-CoV-2 infection.
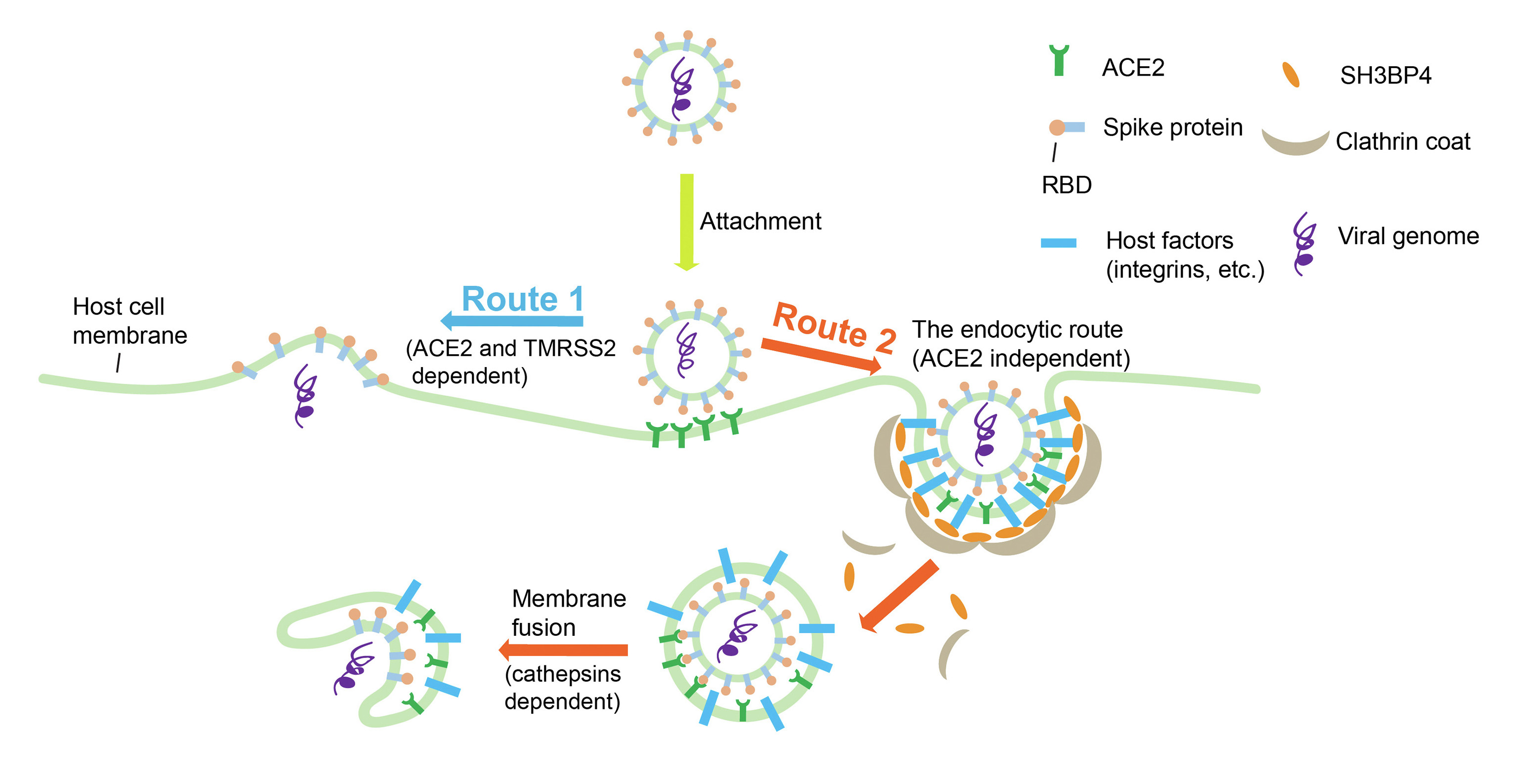
It is generally believed that SARS-CoV-2 enters host cells through the interaction between its spike protein's receptor-binding domain (CoV2-RBD) and the host cell receptor ACE2, facilitating viral invasion. However, most evidence is based on the overexpression of ACE2 to promote viral entry, with few studies conducted on whether completely knocking out ACE2 inhibits viral entry. To address this, the HKUST research team, led by Prof. Guo, in collaboration with research teams from the University of Hong Kong (HKU) and the Hong Kong Polytechnic University (PolyU), has identified other novel surface-located host factors, apart from ACE2, that also bind to CoV2-RBD using the GST pull-down method.
The experiment demonstrates that among the factors, one in particular called SH3BP4, regulates the internalization of CoV2-RBD and mediates the entry of SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus in a manner that is dependent on integrins and the clathrin, but not on ACE2, implying that SH3BP4 promotes viral entry via the endocytic pathway. Many identified factors, including SH3BP4, ADAM9, and TMEM2, show a stronger affinity for CoV2-RBD compared to the RBD of the less infectious SARS-CoV, indicating their specific usage for SARS-CoV-2. Moreover, this study uncovers factors that preferentially bind to the RBD of the SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant, potentially enhancing its entry.
“These findings identify novel host cell surface factors involved in the invasion of SARS-CoV-2 and highlight the crucial role of integrins in mediating viral internalization, establishing new research foundations for treating COVID-19,” Prof. Guo said.
The study was recently published in the international academic journal, Journal of Biological Chemistry. The research team also consists of Prof. CHEN Honglin from Department of Microbiology at HKU; and Prof. YAO Zhongping, from Department of Applied Biology and Chemical Technology at PolyU; and their team members.