HKUST Identifies a Novel Protein in Muscle Stem Cells Fuelling hopes for Stem Cell Treatments for Muscular Dystrophy
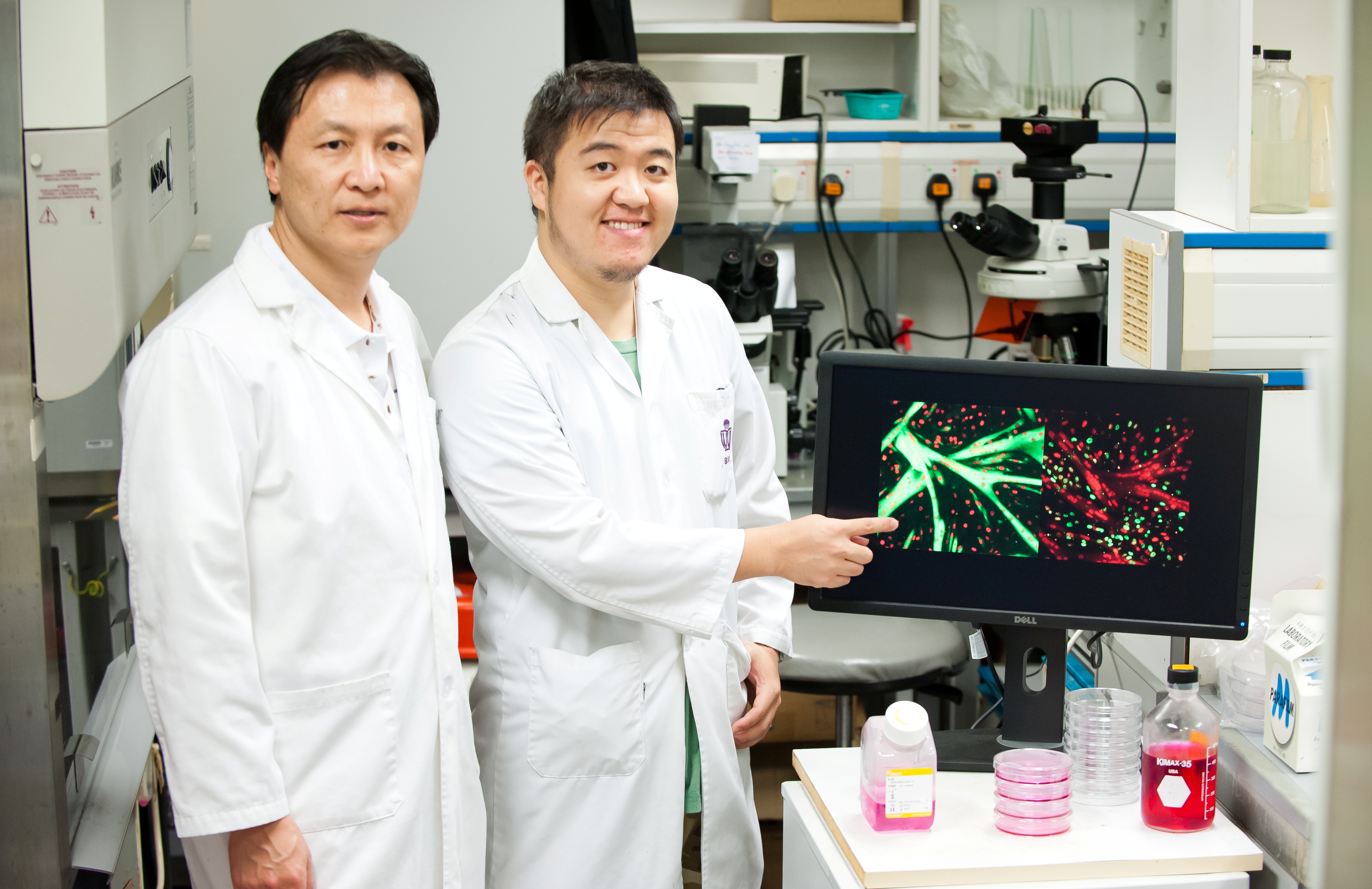
Prof Zhenguo Wu of the Division of Life Science at the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) and his research team have discovered a novel protein Pax3/7BP that plays an influential role in skeletal muscle stem cells. This groundbreaking discovery could lead to more effective stem cell treatments for various muscle diseases including muscular dystrophy.
Skeletal muscle stem cells function differently at different developmental stages. They are responsible for normal skeletal muscle growth in young animals including humans and for injury-induced muscle regeneration in adult animals. In skeletal muscle tissues, Pax7 is a protein that is uniquely present in muscle stem cells and is indispensable for muscle stem cell functions in young animals. However, until recently how Pax7 regulates the functions of muscle stem cells had remained unclear.
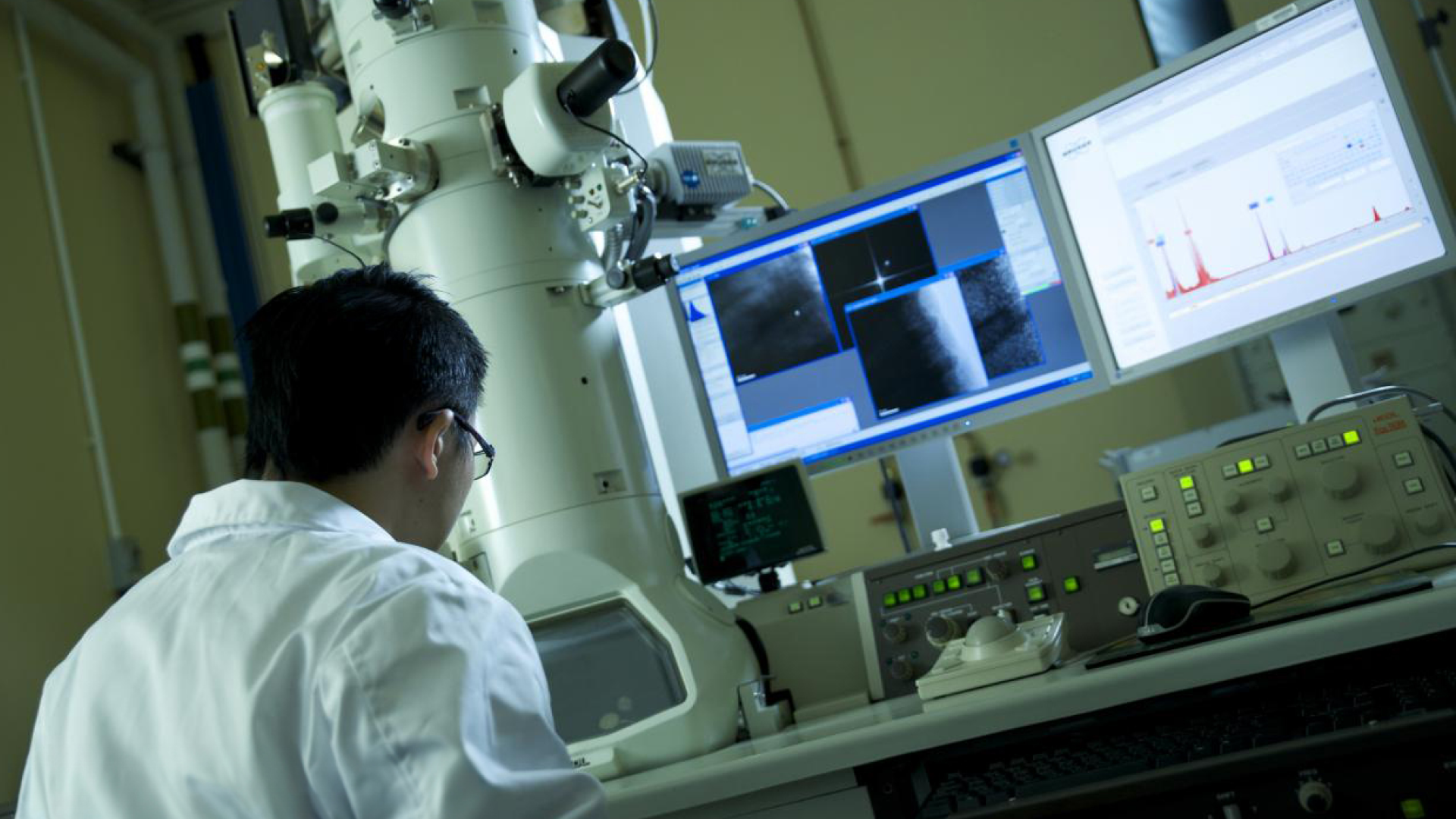
To better understand the functions of Pax7 in muscle stem cells, Prof Wu and his research team have set out to look for Pax7-interacting proteins. Using a technique called yeast two-hybrid screening, they succeeded in identifying a previously uncharacterized Pax7-interacting protein and named it Pax7- and Pax3-binding protein (or Pax3/7BP). Using a series of molecular, cellular, and animal-based assays, the research team found that both Pax7 and Pax3/7BP are required for the proliferation of muscle stem cells in young animals. Mechanistically, Pax3/7BP serves as a key adaptor linking Pax7 with a specific histone-modifying enzyme complex, which is essential for Pax7 to regulate the expression of its target genes. Two of such Pax7 target genes were indeed found to be co-regulated by Pax3/7BP and the histone-modifying enzyme and required for the proliferation of muscle stem cells.
These new findings have inspired a deeper understanding amongst scientific researchers in the role played by Pax7 in muscle stem cells. The breakthrough discovery will facilitate the development of muscle stem cell-based therapies for the treatment of muscle diseases including different forms of muscular dystrophy; for speeding up muscle regeneration after muscle injuries and for improving muscle strength and functions in elderly people. The above findings have been published in the latest issue of Cell Stem Cell, a leading biomedical journal on stem cell research.
This project was led by Dr Yarui Diao, a postdoctoral fellow from the Shenzhen PKU-HKUST Medical Center under the supervision of Prof Zhenguo Wu, in collaboration with other members from both Prof Wu’s laboratory at HKUST and Profs Huating Wang and Hao Sun’s laboratories at the Chinese University of Hong Kong. It was supported by the Hong Kong Research Grant Council and HKUST’s State Key Laboratory on Molecular Neuroscience.
Paper “Pax3/7BP Is a Pax7- and Pax3-Binding Protein that Regulates the Proliferation of Muscle Precursor Cells by an Epigenetic Mechanism“: http://www.cell.com/cell-stem-cell/issue?pii=S1934-5909(12)X0009-2
For media enquiries, please feel free to contact :
Mavis Wong
Tel: 2358 6306
Email: maviswong@ust.hk