Researchers of the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) recently uncovered a novel molecular mechanism that regulates the subcellular localizations of Arf proteins, shedding light on the mechanism underlying various inherited diseases and offering new insight to the treatment of them.
The small GTPases of the ADP-ribosylation factor (Arf) family are key initiators of various physiological processes including secretion, endocytosis, phagocytosis and signal transduction. Arf family proteins function to mediate recruitment of cytosolic effectors to specific subcellular compartments. This process facilitates Arf effectors to perform cargo recognition, lipid modification or other cellular functions. Blocking the activities of Arf family proteins inhibits secretion of important molecules from the cell and also inhibits cellular uptake of nutrients. Defects in Arfs or their regulatory proteins are related to various inherited diseases, including X-linked intellectual disability (XLID), Joubert syndrome, Bardet-Biedl syndrome and cilia dysfunction. Thus, studying molecular mechanisms of Arf-regulated intracellular activities represents an opportunity to understand these diseases’ etiology and develop novel therapeutic strategies.
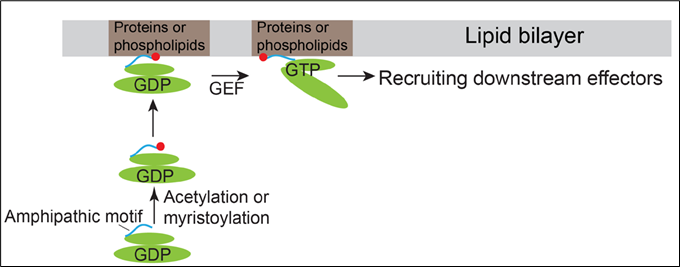
Arf family proteins cycle between a GDP-bound inactive state and a GTP-bound active state. They have similar structural organizations containing an N-terminal amphipathic helix motif and the switch domains. The switch domains of Arf proteins directly bind their corresponding guanidine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs), thus enabling Arf proteins to bind GTP. It is generally conceived that membrane recruitment of Arf proteins are initiated by GTP-binding induced conformational changes of Arf proteins.
In addition to this conventional mechanism, Prof. Guo and his team discovered that the N-terminal amphipathic motifs of the Golgi-localized Arf family protein, Arfrp1, and the endosome- and plasma membrane-localized Arf family protein, Arl14, are sufficient to determine specific subcellular localizations in a GTP-independent manner. Exchanging the amphipathic helix motifs between these two Arf proteins causes the switch of their localizations. The spatial determination mediated by the Arfrp1 helix requires its binding partner Sys1. In addition, the study indicates that the acetylation of the Arfrp1 helix and the myristoylation of the Arl14 helix are important for the specific subcellular localization. A proposed model represents the membrane recruitment of Arfrp1 and Arl14 is shown in Figure 1.
These study uncovers novel insight into the molecular machinery that regulates membrane association of some Arf proteins, suggesting that that the membrane association and activation of some Arf proteins are uncoupled. This study also offers novel short motifs for targeting proteins to specific intracellular localizations.
The findings were recently published in scientific journal Journal of Biological Chemistry.

Prof. Guo is a leading expert on intracellular trafficking. Mr. Feng Yang, a PhD student in his lab, is the first author of this study. This research was funded by the Research Grants Council (RGC) of Hong Kong and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC).